-
Who Bcs Classification

Since the biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS) was introduced in 1995, it has had an increasing impact on regulatory practice. The BCS presented a new paradigm in bioequivalence, based on scientific principles. The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) and Biowaivers Focus Group is part of FIP's Special Interest Group on Regulatory Sciences. Our mission is to.
Bcs classification system. 1. BIOPHARMACEUTICS CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM. Contents. Introduction.
Overview of the Classification system. Applications. Conclusion.
References. Introduction ۞Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)♥ Scientific framework for classifying drug substances based on their aqueous solubility and intestinal permeability What is the need for a classification based on biopharmaceutics of the drug? Its importance in determining bioavailability. ORAL ROUTE♠ Route of choice for the formulators Continues to dominate the area of drug delivery technologies. LIMITATIONS Absorption and Bioavailability in the milieu of gastrointestinal tract. Limitations more prominent with the advent of protein and peptide drugs compounds emerging as a result of combinatorial chemistry and the technique of high throughput screening. API structure salt form and excipients Bioavailability of drug is determined byextent of drug solubility and permeability drug solubility drug product quality attributes. Biopharmaceutics Classification System Guidance provided by the U.S.
Food and Drug Administration for predicting the intestinal drug absorption The fundamental basis established by Dr. Gordon Amidon Distinguished Science Award (Aug ’06,FIP) First introduced into regulatory decision-making process in the guidance document on Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Scale Up And Post Approval Changes. Drug development tool that allows estimation of the contributions of 3 major factors, that affect oral drug absorption from immediate release solid oral dosage forms Dissolution Solubility Intestinal permeability. Pokemon emerald randomized rom.
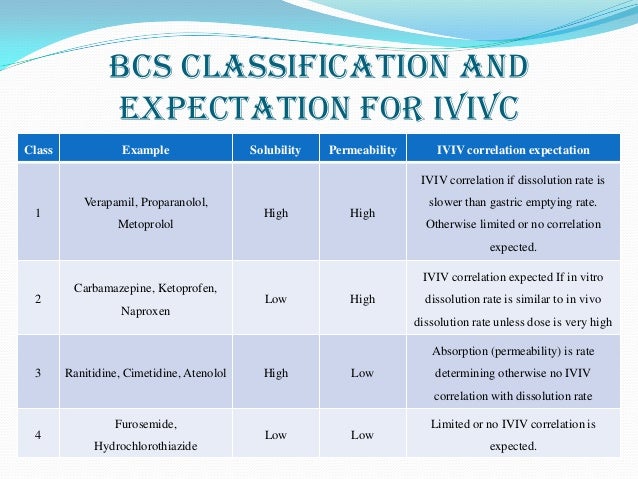
Contents. BCS classes According to the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) drug substances are classified to four classes upon their solubility and permeability:. Class I - high, high. Example:. Those compounds are well absorbed and their absorption rate is usually higher than excretion. Class II - high permeability, low solubility.
Miss pooja mp3 download new song. Example:, paracetamol,. The of those products is limited by their solvation rate. A correlation between the bioavailability and the solvation can be found. Class III - low permeability, high solubility. Example:.
The absorption is limited by the permeation rate but the drug is solvated very fast. If the formulation does not change the permeability or gastro-intestinal duration time, then class I criteria can be applied. Class IV - low permeability, low solubility. Example:. Those compounds have a poor bioavailability. Usually they are not well absorbed over the intestinal mucosa and a high variability is expected.
Definitions The drugs are classified in BCS on the basis of solubility, permeability, and dissolution. Solubility class boundaries are based on the highest dose strength of an immediate release product. A drug is considered highly soluble when the highest dose strength is soluble in 250 ml or less of aqueous media over the pH range of 1 to 7.5. The volume estimate of 250 ml is derived from typical bioequivalence study protocols that prescribe administration of a drug product to fasting human volunteers with a glass of water. Permeability class boundaries are based indirectly on the extent of absorption of a drug substance in humans and directly on the measurement of rates of mass transfer across human intestinal membrane.
Alternatively non-human systems capable of predicting drug absorption in humans can be used (such as in-vitro culture methods). A drug substance is considered highly permeable when the extent of absorption in humans is determined to be 90% or more of the administered dose based on a mass-balance determination or in comparison to an intravenous dose. For dissolution class boundaries, an immediate release product is considered rapidly dissolving when no less than 85% of the labeled amount of the drug substance dissolves within 15 minutes using USP Dissolution Apparatus 1 at 100 RPM or Apparatus 2 at 50 RPM in a volume of 900 ml or less in the following media: 0.1 N HCl or simulated gastric fluid or pH 4.5 buffer and pH 6.8 buffer or simulated intestinal fluid. See also. References.

